Moles and molar masses
Avogadro constant
- Avogadro constant specifies the ammount of particles in a mole of any substance
- it is defined as the number of atoms in precisely 12 grams of
Mole of a substance
- a mole is precisely the Avogadro contant number of particles
- with the weight of an atom, the wieght of a mole increases
- the number of moles of a substance is called ammount of substance
Molar mass
- molar mass is the weight of one mole of a substance
- molar mass of an atom is derived from the relative atomic weight (which can be found in the periodic table)
- relative atomic weight
- molar mass specifies the weight of a mole of a substance composed of either single atoms or molecules
- relative atomic weight
- molar mass of a molecule is the sum of relative atomic weights of its individual atoms
Relationships
- calculating the mass of a substance
- thus:
- calculating the number of particles
- thus:
Elemental composition of pure substances
Denoting elements
- writing down the composition of paticles combines using letters (the symbols of elements) and numbers
- numbers are written in four indexes around the symbol of the element
- top right index denotes the overall charge of the prticle
- bottom right index denotes the number of atoms constituting the particle
- bottom left index denotes the number of protons
- to left index denotes the overall number of nucleons
- it is also reffered to as the mass number
- ex.
Denoting pure substances
Structural formula
- structural formulae denote every atom and bond of the substance
- some formulae also add free electron pairs
- ex.
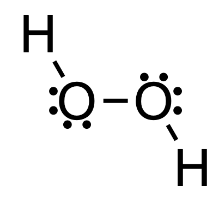
- the structural formula is sometimes condensed
- groups of distinct physical or chemical properties are written together
- ex. Condensed strucural formula of hydrogen peroxide
- it is most commonly used in organic chemistry
Molecular formula
- molecular formulae denote only the numbers of atoms in the substance
- ex. Molecular formula of hydrogen peroxide
- it is most commonly used in inorganic chemistry
Empirical formula
- empirical formulae denote only the most simplified ratios of individual atoms compared to one another
- it is based on simple observations of an unknown substance (hence the name) that determine which atoms can be found in a substance
- it also obeys the law od definite proportions
The simple ratio of atoms in any sample of a pure substance is always preserved.
- ex. Empirical formula of hydrogen peroxide
- it omits all structural descriptors and thus can lead to confusion and misrepresentation
Mass fraction
- mass fraction tells us the fraction of mass a component of a substance takes up
- where: